
- wangg6@rpi.edu
- 0000-0002-2656-7705
About
Ge Wang (Fellow, IEEE, SPIE, AAPM, OSA, AIMBE, AAAS, and NAI) is the Clark & Crossan Endowed Chair Professor and Director of the Biomedical Imaging Center at Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute (Troy, New York, USA). He pioneered the cone-beam spiral CT method in 1991 and published the first perspective on AI-based tomographic imaging in 2016. His other notable contributions, in collaboration with his peers, include interior tomography, bioluminescence tomography, and innovative photon-counting CT algorithms. Dr. Wang's interests encompass AI-based imaging, teaching, and publishing. His recent honors include the 2021 IEEE EMBS Career Achievement Award, 2022 SPIE Meinel Technology Award, 2022 Sigma Xi Chubb Award for Innovation, 2023 RPI Wiley Distinguished Faculty Award, 2023 IEEE R1 Outstanding Teaching Award, 2023 IEEE NPSS/NMISC Hoffman Medical Imaging Scientist Award, 2024 IEEE TRPMS Best Paper Award, and 2025 AAPM Edith H. Quimby Award for Lifetime Achievement. As the Editor-in-Chief of IEEE TMI, Dr. Wang is committed to upholding TMI's tradition of excellence and advancing the “AI4TMI” initiative in collaboration with the global medical imaging community.
Ph.D. Electrical and Computer Engineering, University of Buffalo, New York, USA
M.S. Remote Sensing, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, China
B.E. Signal Processing, Xidian University, Xi'an, China
Research
First paper on spiral/helical cone-beam/multi-slice CT (1991). There are over 200-million CT scans annually worldwide, with a majority in the spiral cone-beam/multi-slice mode. Many follow-up papers along this direction, including superiority of spiral fan-beam CT over step-and-shoot CT (1994) and triple-source helical cone-beam reconstruction (2010)
Bioluminescence tomography (2004) for optical preclinical & biological imaging
Interior tomography (2007) solving the interior problem for targeted imaging at low dose, and fast speed
State-of-the-art multi-scale CT facility (2009) covering six orders of magnitude in terms of image resolution & object size
Omni-tomography (2011) for spatiotemporal fusion of tomographic modalities, with simultaneous CT-MRI as an example
Spectrography (2011) for ultrafast & ultrafine tomography from polychromatic radiation scattering (In Focus News in Nature)
Axiomatic bibliometrics (2013) to credit coauthors (PNAS)
Deep imaging perspective (2016) as the 1st roadmap for this emerging field and a basis for the 1st (2018) and 2nd (2021) dedicated IEEE TMI special issues (over the past 5 years, NIH funding to deep imaging has increased by 3.7X, over $1.1B)
IOP textbook on machine learning for tomographic reconstruction (410 pages, 2019)
National Academy of Inventors (2019, inducted for contributions to spiral cone-beam/multi-slice CT)
Deep denoising network (2019) competitive over commercial low-dose CT (Nature Machine Intelligence)
Deep tomographic reconstruction (2020) (Nature Machine Intelligence)
Deep radiomics (2021) predicting heart diseases with low-dose lung CT (Nature Communications)
IOP Book Series Editor "AI in Biomedicine" (2021-)
Best image clustering results in the world with our SPICE network (https://paperswithcode.com (2021-)
Healthcare metaverse (2022) (Nature Machine Intelligence)
Artificial biological intelligence (2023) (Nature Machine Intelligence)
First place in the AAPM Deep Generative Modeling Grand Challenge (2023)
First CT multimodal multitask foundation model for specialty-oriented generalist medical AI (SOGMAI) (2024)
Bibliometrics: Wang has >600 journal papers (1 in Nature (also reported in Nature as “In Focus News”), 5 in Nature Machine Intelligence, 1 in Nature Communications, 3 in PNAS, 1 in J of Informetrics (reported in Science and Nature), 1 in Phys. Rev. Letters, and >100 in IEEE journals), Google H-index=90, >100 issued and pending patents, >$40M as PI/Contact PI/MPI, and >$39M as Co-PI/Co-I/Mentor.
CT, Multimodality Imaging, AI, Deep Learning
Teaching
- Professor Wang developed the first undergraduate and graduate courses on medical imaging in the deep learning framework and promotes online teaching. He gave numerous talks and seminars internationally, including the 2021 SPIE O+P Plenary on deep imaging and popular science talks on CT and AI. His TEDEd lesson “How X-rays see through your skin” received more than 1.5M views. The book he and his coauthors wrote on "Machine Learning for Tomographic Imaging" is the first in the field and received over 33K downloads in the first three months. More presentations include AI@NIH, MRI, AI-Plenary, AI-Keynote, CT4Layman, AI@Stanford, AI-Stability, SPIE Plenary, SPIE Plenary Interview, Shanghai Tech BME, Sigma Xi Chubb Award Speech, IEEE NPSS Medical Imaging Award Speech, YouTube and B-station.
Recognition
- Fellow of the American Institute for Medical and Biological Engineering “for seminal contributions to the development of single-slice spiral, cone-beam spiral, and micro-CT”, 2002
- Fellow of the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers "for contributions to x-ray tomography", 2003
- Life-time Fellow of the International Society for Optical Engineering “for specific achievements in bioluminescence tomography and x-ray computed tomography”, 2007
- Fellow of the Optical Society of America “for pioneering contributions to development of bioluminescence tomography”, 2009
- Fellow of the American Association of Physics in Medicine “for contributions to medical physics”, 2012
- Fellow of the American Association for the Advancement of Science “for distinguished contributions to the field of biomedical imaging, particularly for x-ray computed tomography, optical molecular tomography, interior tomography, and multi-modality fusion”, 2014
- Life-time Fellow of the National Academy of Inventor “for contributions to spiral/helical cone-beam/multi-slice CT”, 2029
- Giovanni DiChiro Award for Outstanding Scientific Research. Journal of Computer Assisted Tomography, 1997
- Medical Physics Travel Award. American Association of Physicists in Medicine and Institute of Physics and Engineering in Medicine (1 per year in USA to lecture in Europe for 2-3 weeks to promote interaction between USA and Europe). AAPM/IPEM, 1999
- Herbert M. Stauffer Award for Outstanding Basic Science Paper in Academic Radiology. Association of University Radiologists, USA, 2005
- Dean’s Award for Excellence in Research. College of Engineering, Virginia Tech, 2010
- Goldwater Award (Eugene Katsevich as a mathematics undergraduate with Princeton University for a paper from his summer work in Ge Wang’s lab). Goldwater Education Foundation, 2012
- School of Engineering Outstanding Professor Award. Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute, 2018
- EEE EMBS Academic Career Achievement Award “for pioneering contributions on cone-beam tomography and deep learning-based tomographic imaging.” IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, 2021
- Outstanding Teaching Award “for development of the first graduate and undergraduate deep learning-based medical imaging courses at Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute.” IEEE Region 1, 2021
- World Artificial Intelligence Conference Youth Outstanding Paper Award “for Shan HM, Padole A, Homayounieh F, Kruger U, Khera RD, Nitiwarangkul C, Kalra MK, Wang G, Nature Machine Intelligence 1:269-276, 2019.” World Artificial Intelligence Conference, 2021
- Doctoral Dissertation Award (to Fenglei Fan in recognition of his PhD dissertation entitled “Advanced Neural Networks and Their Interpretation”; Advisor: Ge Wang) as “the best doctoral dissertation in the neural networks, machine learning, and related fields.” International Neural Network Society, 2021
- SPIE Aden & Marjorie Meinel Technology Achievement Award “for contributions in X-ray and optical molecular tomography, including their coupling for biomedical applications.” SPIE, 2022
- Walston Chubb Award for Innovation “for pioneering contributions to medical imaging and major impacts on research, development, and healthcare, including his cone-beam CT method and AI-based imaging leadership.” Sigma Xi, 2022
- William H. Wiley Distinguished Faculty Award "for outstanding teaching, productive research, service to Rensselaer, contributions to professional organizations, and community involvement." Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute, 2023
- Edward J. Hoffman Medical Imaging Scientist Award "for pioneering contributions to medical computed tomography, multi-modality imaging, and AI-based tomographic imaging, as well as exemplary mentorship in medical imaging training and education." IEEE NPSS, 2023
- IEEE TRPMS Best Paper Award for F. -L. Fan, J. Xiong, M. Li and G. Wang, "On Interpretability of Artificial Neural Networks: A Survey," IEEE Transactions on Radiation and Plasma Medical Sciences, vol. 5, pp. 741-760, 2021. IEEE NSS/MIC, 2024
- AAPM Edith H. Quimby Award for Lifetime Achievement including “outstanding scientific achievements in medical physics, significant influence on the professional development of others, and impactful organizational leadership”, American Association of Physicists in Medicine, 2025
Publications
The following is a selection of recent publications in Scopus. Ge Wang has 786 indexed publications in the subjects of Medicine, Engineering, Computer Science.
News
Wiki Biography
Ge Wang’s Biography on Wikipedia
Ge Wang (Chinese name 王革; born in 1957) is a medical imaging scientist focusing on computed tomography (CT), multimodality imaging, and artificial intelligence especially deep learning. He is the Clark & Crossan Chair Professor of Biomedical Engineering and the Director of the Biomedical Imaging Center, Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute, Troy, New York, USA. His URLs include Profile; Lab, Google Scholar, YouTube, and B Station.
Career Achievements
Most Impactful Work – Spiral Cone-beam CT
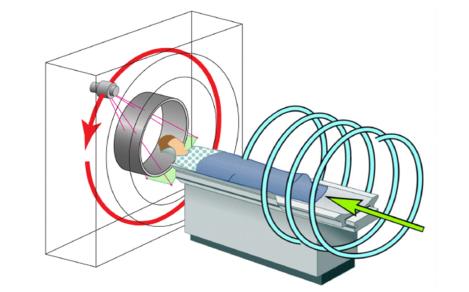
He pioneered the spiral cone-beam CT method in 1991. His work on spiral cone-beam CT solves "the long object problem" (longitudinal data truncation) and has a major impact on the CT field. Defrise et al. wrote that “to solve the long-object problem, a first level of improvement with respect to the 2D filtered backprojection algorithms was obtained by backprojecting the data in 3D, along the actual measurement rays. The prototype of this approach is the algorithm of Wang et al.” La Riviere and Crawford wrote that “most commercial systems used approximate methods based on extending the Feldkamp–Davis–Kress reconstruction to helical cone-beam scanning trajectories initially formulated by Wang et al.” For this work, he was inducted to the National Academy of Inventors in 2019. He and his collaborators published many papers on spiral cone-beam CT, including exact cone-beam reconstruction with a general trajectory, a quasi-exact triple-source cone-beam reconstruction, and more. Currently, there are ~200 million medical CT scans yearly with a majority in this scanning mode.
AI-empowered Breakthrough – Deep Tomographic Imaging
In 2016, he presented the first roadmap on deep tomographic imaging. With his collaborators he published a series of papers in this new area of image reconstruction, including major results on deep denoising, deep reconstruction, deep radiomics, and healthcare metaverse. With his coauthors, he published the first book on machine learning-based tomographic reconstruction in 2019 (IOP Top Download, more than 33,000 in 2020), and edited two special issues on this theme for IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging. In partnership with General Electric, FDA and other leading institutions, his team develops deep imaging algorithms and systems for clinical and preclinical applications.
Other Innovations
He and his collaborators developed interior tomography to solve “the interior problem” (transverse data truncation), and omni-tomography (for spatiotemporal fusion of tomographic modalities, with simultaneous CT-MRI as an example. Also, his team developed bioluminescence tomography for optical molecular imaging and spectrography for ultrafast and ultrafine tomography from polychromatic scattering data. He worked on axiomatic bibliometrics, with results reported in Nature, Science, and news media. Also, he developed the first undergraduate and graduate courses on deep medical imaging and distanced online testing technology.
Societal Fellowships
- Fellow of the American Institute for Medical and Biological Engineering (AIMBE) “for seminal contributions to the development of single-slice spiral, cone-beam spiral, and micro-CT”, 2002
- Fellow of the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers "for contributions to x-ray tomography", 2003
- Life-time Fellow of the International Society for Optical Engineering “for specific achievements in bioluminescence tomography and x-ray computed tomography”, 2007
- Fellow of the Optical Society of America “for pioneering contributions to development of bioluminescence tomography”, 2009
- Fellow of the American Association of Physics in Medicine “for contributions to medical physics”, 2012
- Fellow of the American Association for the Advancement of Science “for distinguished contributions to the field of biomedical imaging, particularly for x-ray computed tomography, optical molecular tomography, interior tomography, and multi-modality fusion”, 2014
- Life-time Fellow of the National Academy of Inventor “for contributions to spiral/helical cone-beam/multi-slice CT”, 2019
Selected Research and Teaching Awards
- Fellow of the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers "for contributions to x-ray tomography", 2003
- Giovanni DiChiro Award for Outstanding Scientific Research, Journal of Computer Assisted Tomography, 1997
- APPM/IPEM Medical Physics Travel Award, American Association of Physicists in Medicine and Institute of Physics and Engineering in Medicine (one person per year) in USA to lecture in Europe for two to three weeks), 1999
- Herbert M. Stauffer Award for Outstanding Basic Science Paper in Academic Radiology, Association for University Radiologists, USA, 2005
- Dean's Award for Excellence in Research, College of Engineering, Virginia Tech, 2010
- Goldwater Award; Eugene Katsevich as an undergraduate with Princeton University for a paper from his summer intern work in Ge EWang's lab), 2012
- School of Engineering Outstanding Professor Award (one person per year), Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute, 2018
- IEEE EMBS Academic Career Achievement Award (one person per year) "for pioneering contributions on cone-beam tomography and deep learning-based tomographic imaging," IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, 2021
- IEEE Region 1 Outstanding Teaching Award (one person per year) "for development of the first graduate and undergraduate deep learning-based medical imaging courses at Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute," IEEE, 2021
- World Artificial Intelligence Conference Youth Outstanding Paper Award "for Shan HM, Padole A, Homayounieh F, Kruger U, Khera RD, Nitiwarangkul C, Kalra MK, Wang G, Nature Machine Intelligence 1:269-276, 2019," World Artificial Intelligence Conference, 2021
- SPIE Aden & Marjorie Meinel Technology Achievement Award (one person per year) "for contributions in X-ray and optical molecular tomography, including their coupling for biomedical applications," SPIE, 2022
- Sigma Xi Walston Chubb Award for Innovation “for pioneering contributions to medical imaging and major impacts on research, development, and healthcare, including his cone-beam CT method and AI-based imaging leadership.” Sigma Xi, 2022
- William H. Wiley Distinguished Faculty Award (for outstanding teaching, productive research, service to Rensselaer, contributions to professional organizations, and community involvement). Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute, 2023
- Edward J. Hoffman Medical Imaging Scientist Award "for pioneering contributions to medical computed tomography, multi-modality imaging, and AI-based tomographic imaging, as well as exemplary mentorship in medical imaging training and education." IEEE NPSS, 2023
Publications, Funding, and Presentations
In addition to conference/arXiv papers, he has more than 600 peer-reviewed papers in PNAS, Nature Machine Intelligence, Nature Communications, Nature, and other well-known journals, as well as over 100 issued and pending patents. He has been continuously well-funded by NIH, NSF, and industry (more than $40 million as PI/Contact PI/MPI, and more than $39 million as Co-PI/Co-I/Mentor). He gave numerous seminars, keynotes and plenaries internationally, including the 2021 SPIE O+P Plenary on deep imaging. His TEDEd lesson, "How X-rays see through your skin," received more than 1.8 million views.
Employment
- Department of Electrical Engineering, Graduate School of Academia Sinica, China;
- Mallinckrodt Institute of Radiology, Washington University in St. Louis, USA;
- Department of Radiology, University of Iowa, USA;
- School of Biomedical Engineering and Sciences, Virginia Tech and Wake Forest University, USA;
- Department of Biomedical Engineering, Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute, USA
Alma Mater
- Xidian University, BE, China;
- Graduate School of Academia Sinica, MS, China;
- University of Buffalo, MS, PhD, USA
References
- Reich ES: Three-dimensional technique on trial, Nature, In-Focus News, December 14, 2011
- Wang G., Liu F., Liu FL, Cao GH, Gao H, Vannier MW: Design proposed for a combined MRI/computed-tomography scanner. SPIE Newsroom: 10.1117/2.1201305.004860, 2013
- Dineley J: Tackling the silent crisis in cancer care, for the Nobel Laureate Meeting, August 1, 2018
- Freeman T: Machine learning for tomographic imaging, Jan. 30, 2020
- Wells T: In era of online learning, new testing method aims to reduce cheating, Science Daily, March 1, 2021
- Hamilton R: Ge Wang receives 2021 EMBS Academic Career Achievement Award, June 17, 2021
- Thomas K. Inventing the future at his AI-based X-ray Imaging System lab, July 9, 2021
- Jacques A: Ge Wang – The SPIE Aden & Marjorie Meinel Technology Achievement Award, January 11, 2022
- Wang G: Future of Medical Imaging, Nov. 4, 2022
- Malatino K: Artificial Biological Intelligence Could Play a Key Role in the Future, June 2, 2023
- Malatino K: RPI Professor Is Honored for Medical Imaging Research, Contributes to American Scientist. Oct. 2, 2023